You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Monitoring Using CoreOS Prometheus Operator
CoreOS prometheus-operator provides simple and Kubernetes native way to deploy and configure Prometheus server. This tutorial will show you how to use CoreOS Prometheus operator for monitoring Stash.
Before You Begin
At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using Minikube.
To keep Prometheus resources isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace to deploy Prometheus operator and respective resources.
$ kubectl create ns monitoring namespace/monitoring createdWe need a CoreOS prometheus-operator instance running. If you already don’t have a running instance, deploy one following the docs from here.
Enable Monitoring in Stash
Enable Prometheus monitoring using prometheus.io/coreos-operator agent while installing Stash. To know details about how to enable monitoring see here.
Here, we are going to enable monitoring for both backup & recovery and operator metrics.
$ curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appscode/stash/0.8.2/hack/deploy/stash.sh | bash -s -- \
--monitoring-agent=prometheus.io/coreos-operator \
--monitoring-backup=true \
--monitoring-operator=true \
--prometheus-namespace=monitoring \
--servicemonitor-label=k8s-app=prometheus
This will create a ServiceMonitor crd with name stash-servicemonitor in monitoring namespace for monitoring endpoints of stash-operator service. This ServiceMonitor will have label k8s-app: prometheus provided by --servicemonitor-label flag. This label will be used by Prometheus crd to select this ServiceMonitor.
Let’s check the ServiceMonitor crd using following command,
$ kubectl get servicemonitor stash-servicemonitor -n monitoring -o yaml
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: ServiceMonitor
metadata:
annotations:
kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration: |
{"apiVersion":"monitoring.coreos.com/v1","kind":"ServiceMonitor","metadata":{"annotations":{},"labels":{"k8s-app":"prometheus"},"name":"stash-servicemonitor","namespace":"monitoring"},"spec":{"endpoints":[{"honorLabels":true,"port":"pushgateway"},{"bearerTokenFile":"/var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token","port":"api","scheme":"https","tlsConfig":{"caFile":"/etc/prometheus/secrets/stash-apiserver-cert/tls.crt","serverName":"stash-operator.kube-system.svc"}}],"namespaceSelector":{"matchNames":["kube-system"]},"selector":{"matchLabels":{"app":"stash"}}}}
creationTimestamp: 2018-11-21T09:35:37Z
generation: 1
labels:
k8s-app: prometheus
name: stash-servicemonitor
namespace: monitoring
resourceVersion: "6126"
selfLink: /apis/monitoring.coreos.com/v1/namespaces/monitoring/servicemonitors/stash-servicemonitor
uid: cd6cca14-ed70-11e8-8838-0800272dd258
spec:
endpoints:
- honorLabels: true
port: pushgateway
- bearerTokenFile: /var/run/secrets/kubernetes.io/serviceaccount/token
port: api
scheme: https
tlsConfig:
caFile: /etc/prometheus/secrets/stash-apiserver-cert/tls.crt
serverName: stash-operator.kube-system.svc
namespaceSelector:
matchNames:
- kube-system
selector:
matchLabels:
app: stash
Here, we have two endpoints at spec.endpoints field. One is pushgateway that exports backup and recovery metrics and another is api which exports operator metrics.
Stash exports operator metrics via TLS secured api endpoint. So, Prometheus server need to provide certificate while scrapping metrics from this endpoint. Stash has created a secret named stash-apiserver-certs with this certificate in monitoring namespace as we have specified that we are going to deploy Prometheus in that namespace through --prometheus-namespace flag. We have to specify this secret in Prometheus crd through spec.secrets field. Prometheus operator will mount this secret at /etc/prometheus/secrets/stash-apiserver-cert directory of respective Prometheus pod. So, we need to configure tlsConfig field to use that certificate. Here, caFile indicates the certificate to use and serverName is used to verify hostname. In our case, the certificate is valid for hostname server and stash-operator.kube-system.svc.
Let’s check secret stash-apiserver-cert has been created in monitoring namespace.
$ kubectl get secret -n monitoring -l=app=stash
NAME TYPE DATA AGE
stash-apiserver-cert kubernetes.io/tls 2 31m
Also note that, there is a bearerTokenFile field. This file is token for the serviceaccount that will be created while creating RBAC stuff for Prometheus crd. This is required for authorizing Prometheus to scrape Stash API server.
Now, we are ready to deploy Prometheus server.
Deploy Prometheus Server
In order to deploy Prometheus server, we have to create Prometheus crd. Prometheus crd defines a desired Prometheus server setup. For more details about Prometheus crd, please visit here.
If you are using a RBAC enabled cluster, you have to give necessary permissions to Prometheus. Check the documentation to see required RBAC permission from here.
Create Prometheus:
Below is the YAML of Prometheus crd that we are going to create for this tutorial,
apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
kind: Prometheus
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: monitoring
labels:
k8s-app: prometheus
spec:
replicas: 1
serviceAccountName: prometheus
serviceMonitorSelector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: prometheus
secrets:
- stash-apiserver-cert
resources:
requests:
memory: 400Mi
Here, spec.serviceMonitorSelector is used to select the ServiceMonitor crd that is created by Stash. We have provided stash-apiserver-cert secret in spec.secrets field. This will be mounted in Prometheus pod.
Let’s create the Prometheus object we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/appscode/stash/0.8.2/docs/examples/monitoring/coreos/prometheus.yaml
prometheus.monitoring.coreos.com/prometheus created
Prometheus operator watches for Prometheus crd. Once a Prometheus crd is created, Prometheus operator generates respective configuration and creates a StatefulSet to run Prometheus server.
Let’s check StatefulSet has been created,
$ kubectl get statefulset -n monitoring
NAME DESIRED CURRENT AGE
prometheus-prometheus 1 1 4m
Check StatefulSet’s pod is running,
$ kubectl get pod prometheus-prometheus-0 -n monitoring
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
prometheus-prometheus-0 2/2 Running 0 6m
Now, we are ready to access Prometheus dashboard.
Verify Monitoring Metrics
Prometheus server is running on port 9090. We are going to use port forwarding to access Prometheus dashboard. Run following command on a separate terminal,
$ kubectl port-forward -n monitoring prometheus-prometheus-0 9090
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9090 -> 9090
Forwarding from [::1]:9090 -> 9090
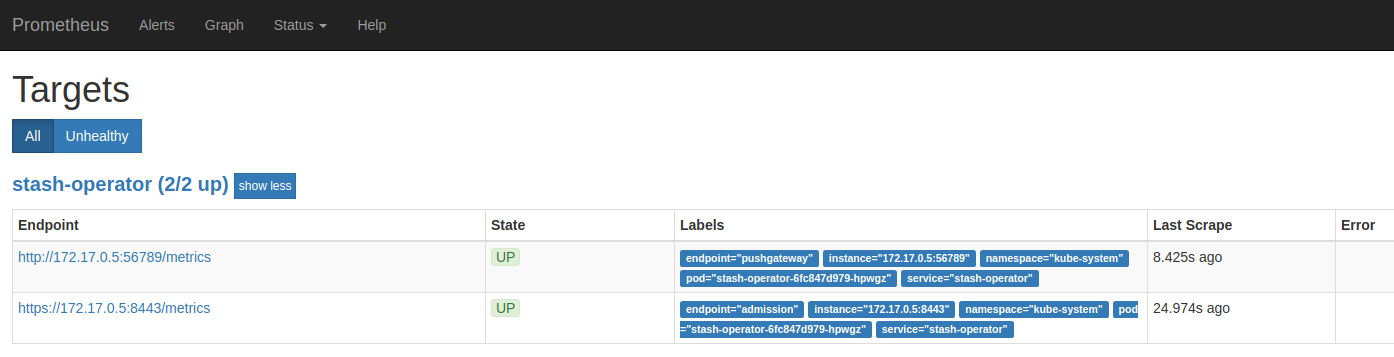
Now, we can access the dashboard at localhost:9090. Open http://localhost:9090 in your browser. You should see pushgateway and api endpoints of stash-operator service as target.
Cleanup
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
# cleanup Prometheus resources
kubectl delete -n monitoring prometheus prometheus
kubectl delete -n monitoring secret stash-apiserver-cert
# delete namespace
kubectl delete ns monitoring
To uninstall Stash follow this guide.




















