New to Stash? Please start here.
Stash Backends
Stash supports various backends for storing data snapshots. It can be a cloud storage like GCS bucket, AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage etc. or a Kubernetes persistent volume like HostPath, PersistentVolumeClaim, NFS etc.
The following diagram shows how Stash sidecar container accesses and backs up data into a backend.
You have to create a Repository object which contains backend information and a Secret which contains necessary credentials to access the backend.
Stash sidecar/backup job reads backend information from the Repository and retrieves access credentials from the Secret. Then on the first backup session, Stash will initialize a repository in the backend.
Below, a screenshot that shows a repository created in AWS S3 bucket named stash-qa:
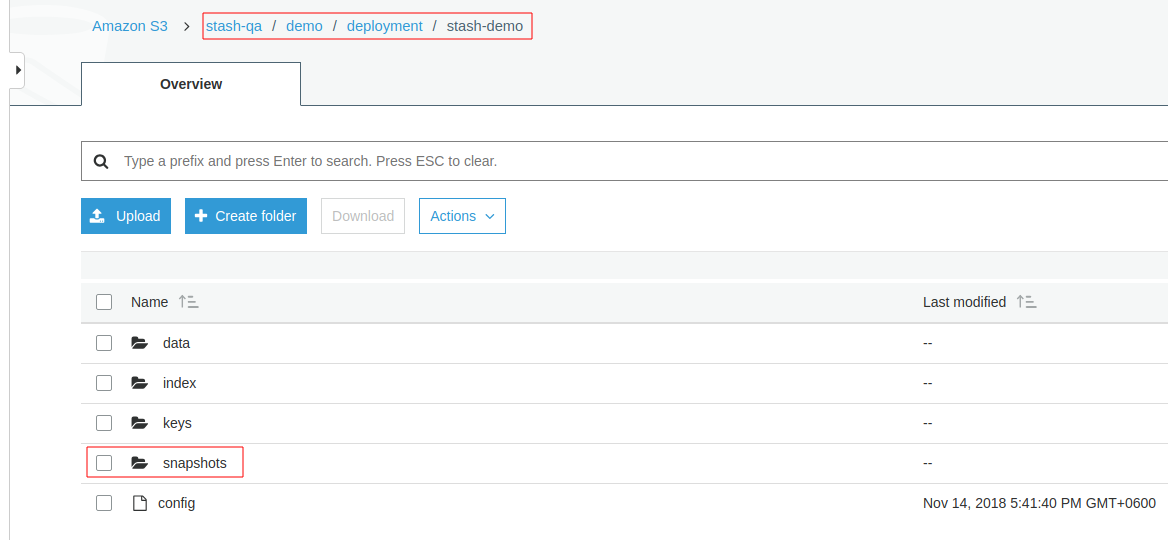
You will see all snapshots taken by Stash at /snapshot directory of this repository.
Note: Stash stores data encrypted at rest. So, snapshot files in the bucket will not contain any meaningful data until they are decrypted.
Next Steps
- Learn how to configure
Kubernetes Volumeas backend from here. - Learn how to configure
AWS S3/Minio/Rookbackend from here. - Learn how to configure
Google Cloud Storage (GCS)backend from here. - Learn how to configure
Microsoft Azure Storagebackend from here. - Learn how to configure
OpenStack Swiftbackend from here. - Learn how to configure
Backblaze B2backend from here. - Learn how to configure
RESTbackend from here.




















