You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
New to Stash? Please start here.
Stash Backends
Stash supports various backends for storing data snapshots. It can be a cloud storage like GCS bucket, AWS S3, Azure Blob Storage etc. or a Kubernetes persistent volume like HostPath, PersistentVolumeClaim, NFS etc.
The following diagram shows how Stash sidecar container accesses and backs up data into a backend.

You have to create a Repository object which contains backend information and a Secret which contains necessary credentials to access the backend.
Stash sidecar/backup job reads backend information from the Repository and retrieves access credentials from the Secret. Then on the first backup session, Stash will initialize a repository in the backend.
Below, a screenshot that shows a repository created in AWS S3 bucket named stash-qa:
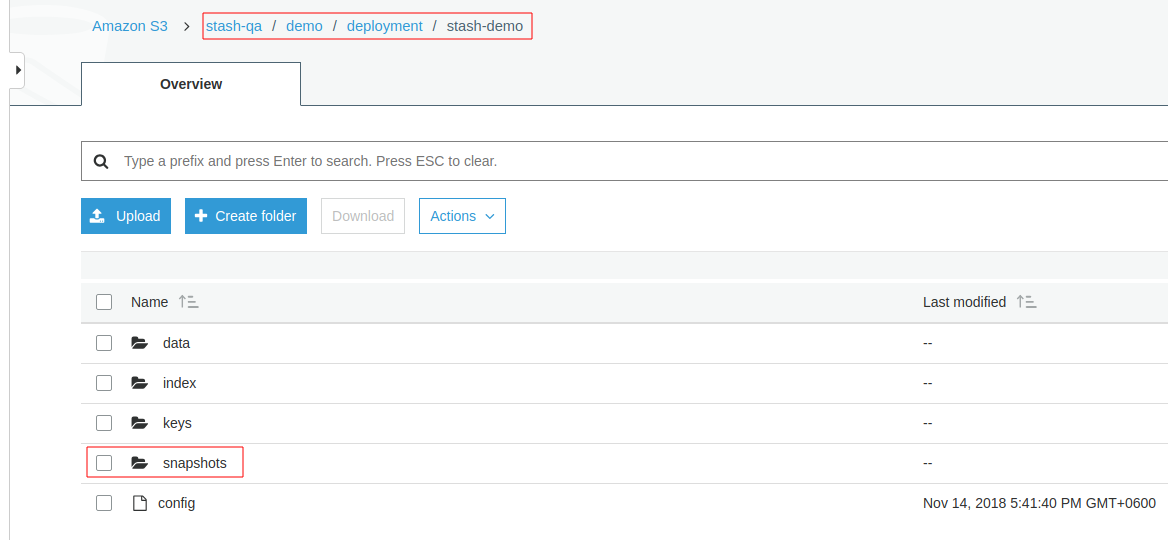
You will see all snapshots taken by Stash at /snapshot directory of this repository.
Note: Stash stores data encrypted at rest. So, snapshot files in the bucket will not contain any meaningful data until they are decrypted.
Next Steps
- Learn how to configure
Kuberntes Volumeas backend from here. - Learn how to configure
AWS S3/Minio/Rookbackend from here. - Learn how to configure
Google Cloud Storage (GCS)backend from here. - Learn how to configure
Microsoft Azure Storagebackend from here. - Learn how to configure
OpenStack Swiftbackend from here. - Learn how to configure
Backblaze B2backend from here. - Learn how to configure
RESTbackend from here.




















